Understanding Athlete's Foot: Common Symptoms and Risks
Athlete's foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a prevalent fungal infection that affects millions worldwide. It typically manifests as dry, flaky skin, particularly on the soles and sides of the feet. Another tell-tale symptom is the white, soggy skin that often appears between the toes. In severe cases, blistering may also occur. The infection thrives in warm, moist environments, making public showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools common sources of contagion.
While the symptoms may start mildly, they can quickly escalate if left untreated. The fungal infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the hands, groin, or even the nails, leading to complications that are more challenging to manage. The contagious nature of the infection also means it can easily be passed on to others, making it essential to address the problem promptly and effectively.
Over-the-Counter Treatments: When Are They Enough?
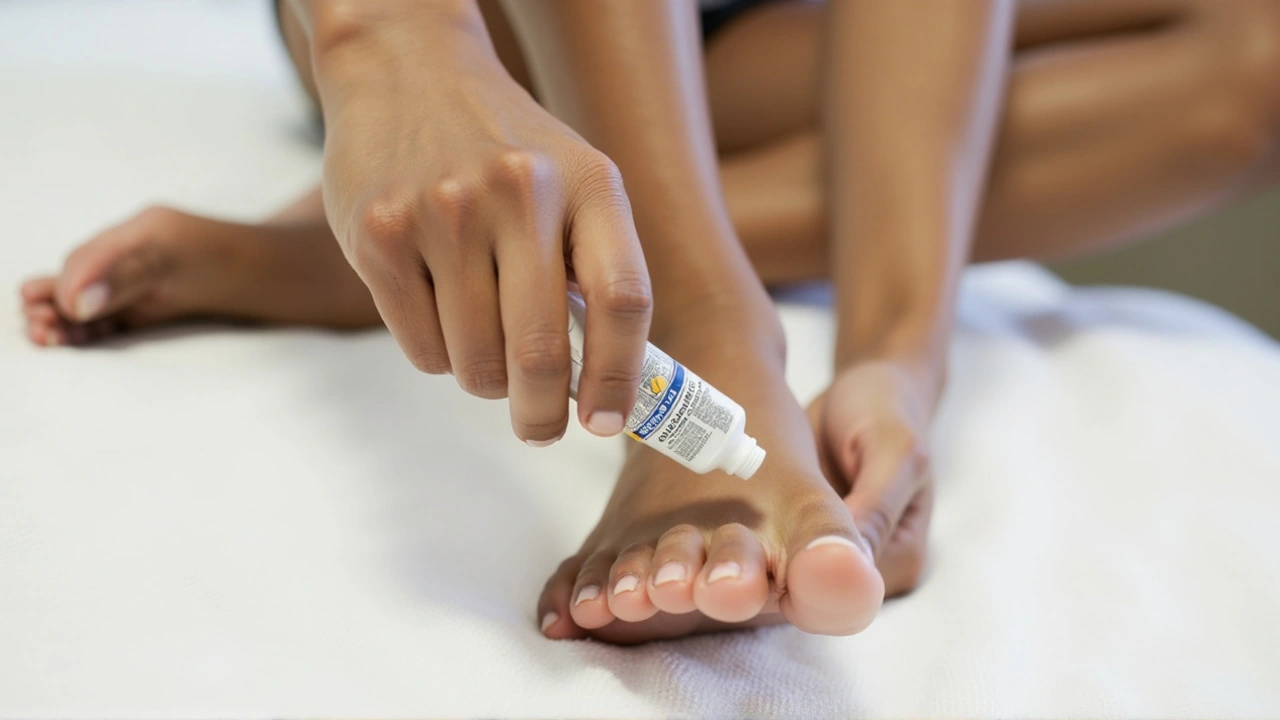
For many individuals, over-the-counter (OTC) treatments are a first line of defense against athlete's foot. Products like Lamisil, Lotrimin, and Tinactin are readily available and can be highly effective in treating mild to moderate cases of the infection. These antifungal creams, sprays, and powders are designed to eliminate the fungus and alleviate symptoms. Instructions on these products typically advise application once or twice daily, depending on the severity of the infection.
Despite their convenience and widespread availability, OTC treatments are not always sufficient. Several factors can influence their effectiveness, including the specific strain of fungus, the extent of the infection, and individual responses to the medication. In cases where symptoms persist or worsen despite diligent use of OTC remedies, it may be time to consider stronger options.
When to Seek Prescription Medication
There are several indicators that it's time to consult a healthcare provider for prescription-strength treatments. If you've been using OTC medications as directed for several weeks with no significant improvement, this is a clear sign that you need more potent intervention. Prescription medications are also warranted in severe cases where the infection has caused extensive discomfort or skin damage.
One of the primary benefits of prescription treatments is their ability to target more resilient strains of fungus. Oral antifungals like terbinafine and itraconazole are commonly prescribed for chronic or widespread infections. These medications work systemically, meaning they travel through the bloodstream to attack the infection from within, providing a more comprehensive solution. For those who cannot take oral medications, topical prescription creams and ointments are also available.
The Role of Proper Foot Hygiene
No matter how effective the medication, proper foot hygiene plays a critical role in both treating and preventing athlete's foot. Regularly washing your feet with soap and water, thoroughly drying them, especially between the toes, and wearing breathable footwear can make a significant difference. It's also advisable to change socks frequently and avoid walking barefoot in public areas known for being breeding grounds for fungi.
Follow-up care is equally important. Once the infection has been treated, continue practicing good hygiene to prevent recurrence. Be mindful of any early signs of infection and act swiftly to address them before they escalate. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help ensure the infection remains under control.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Solution
Athlete's foot is a common but potentially stubborn infection that can range from mildly irritating to intensely painful. While OTC treatments are effective for many, some cases require the intervention of prescription-strength medications. Identifying the need for these stronger treatments can help prevent the spread and escalation of the infection, ensuring better health outcomes. Remember, proper foot hygiene is indispensable in managing and preventing athlete's foot. If you're facing persistent or severe symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider is the best course of action.

Jackson Olsen
August 22, 2024 AT 14:05Penny Clark
August 22, 2024 AT 18:04krishna raut
August 24, 2024 AT 05:58Callum Breden
August 24, 2024 AT 16:26Niki Tiki
August 25, 2024 AT 23:59MOLLY SURNO
August 26, 2024 AT 22:02Emily Kidd
August 28, 2024 AT 09:57Justin Cheah
August 29, 2024 AT 23:18caiden gilbert
August 31, 2024 AT 20:01Jim Allen
September 1, 2024 AT 03:37John Kane
September 1, 2024 AT 05:58Aditya Singh
September 2, 2024 AT 18:37Nate Girard
September 4, 2024 AT 00:19Prakash pawar
September 5, 2024 AT 09:27Carolyn Kiger
September 5, 2024 AT 19:51Katherine Reinarz
September 6, 2024 AT 21:36Erin Corcoran
September 8, 2024 AT 07:31phenter mine
September 9, 2024 AT 07:31Mansi Gupta
September 11, 2024 AT 04:21Alex Hundert
September 12, 2024 AT 20:38